How to reset a laptop battery. HP Notebook PCs - Checking and Calibrating the Battery (Windows)
Thanks to the rechargeable battery, the laptop has become a mobile device. Users often encounter various battery-related problems.
These troubles are distinguished by their complexity, and in some situations you have to visit a service center. However, some shortcomings can be eliminated independently, but for this you need to know the pinout of the laptop battery.
Battery types
All batteries operate on the same principle - the reversibility of the reactions occurring in them. Simply put, a chemical reaction goes in one direction, but the charge goes in the opposite direction.
Today on laptops 2 types of batteries are used:
- Lithium-ion, or Li-Ion.
- , or Li-Pol.
The second type of battery is more modern and is increasingly used by manufacturers. At the beginning of the era of mobile devices, nickel-cadmium batteries were actively used.
However, they contain cadmium, which is highly toxic. As a result, serious problems arose with the disposal of failed batteries.
They were replaced by nickel-metal hydride batteries, which lack some of the disadvantages of nickel-cadmium batteries. But their energy intensity was still low, as was the number of recharge cycles.
Lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density and a low self-discharge rate. However, they are not without a drawback: lithium is gradually destroyed, and after a year the battery capacity decreases. In practice, the service life of batteries of this type is 2-3 years, and not the 5 years declared by the manufacturers.
Battery device
Modern laptop batteries are connected using the SMBus interface. They have a minimum of 5 contacts, two of which are designed to transmit voltage. Two more pins allow you to exchange information about the battery charge level, completed recharge cycles, etc.
The battery consists of the following elements:
- thermostat;
- controller;
- battery cells;
- contact area;
- circuit breakers.
The controller is designed to disconnect the battery from the charger when the maximum charge is reached or when the voltage drops to 2.5 volts.
In the second case, shutdown is necessary to prevent irreversible chemical changes in the batteries. Modern batteries have a large number of sensors installed to ensure reliable protection of the power source.
Pinout diagrams
Modern batteries have from 5 to 9 contacts. The battery pinout for a Samsung laptop or other laptop may vary depending on the model. That is why users are looking for a diagram for their mobile device on the official websites of manufacturing companies.
If the battery has a seven-pin connector, then it The pinout may look like this:
However, it should be remembered that depending on the model, the pinout of the laptop battery from Acer, Lenovo, Toshiba and other manufacturers may differ depending on the specific model.

To find the pinout of a laptop battery from HP, Dell or another company, the user will have to visit the manufacturer's official website.
If you can’t find the necessary information there, you will have to go to the form for owners of laptops from a specific manufacturer.
An example is mu06 notebook battery pinout, used in HP devices.

Resetting the controller
Even if the pinout of the Acer or other manufacturer's laptop battery is known, this may not be enough to resolve the problem. It is equally important to have an idea about the battery controller - this is a microcircuit that interacts with the controller of the motherboard of the laptop itself and transmits to the OS all the necessary information about the operation and condition of the battery.
Here circuit diagram of a laptop battery controller based on the DW 01-З chip.

If the controller starts to work incorrectly, the OS receives incorrect information. As a result, various troubles may arise, for example, the laptop will turn off faster than expected at 100% charge. This behavior of the device does not necessarily indicate a battery failure, and the problem can be solved by resetting the laptop battery controller ().
There are two ways to solve the problem:
- Software.
- Manual.
In the first case, special software is used, for example, the Battery EEPROM Works program. This is a powerful utility that often literally revives the battery.
However, to use it you need to understand microcircuits.
 At home for most users manual calibration is the best choice.
At home for most users manual calibration is the best choice.
If possible, you can use special utilities to manage the power of the laptop from the device manufacturer.
After starting it, you must select the option to reset the controller and strictly follow the instructions.
If such a program was not found, calibration can be done manually. To do this, the laptop is disconnected from the network and switched to BIOS mode. After this, the device must be left turned on until the battery is completely discharged, without turning off the laptop, it must be charged and wait until the battery capacity is fully restored. If these manipulations do not bring the battery back to life, it will have to be replaced.
Let's see what kind of batteries there are in principle:
- NICKEL-CADMIUM BATTERY - (or NiCd for short) nickel-cadmium;
- NICKEL METAL-HYDRIDE BATTERY - (or NiMH for short) nickel-metal hydride;
- LITHIUM ION BATTERY - (or Li-ion for short) lithium-ion batteries.
Lately batteries have been used Li-ion
The first thing you need to do is calibrate the battery. In fact, this is the calibration of the controller.
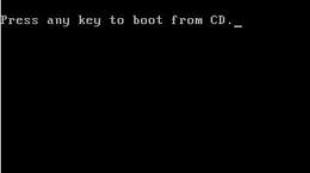
First you need to completely discharge the battery - turn off the power supply, reboot, intercept the boot (so that the OS does not boot) by calling the BIOS setup.
Place the laptop on its end like a slightly open book (for better cooling, with the muzzle up if it is on the side) and leave it until it turns off until the entire battery is drained.
Typically, the controller notes both events (full discharge and full charge), after which it begins to count the charge correctly - until a charge measurement error occurs again.
If all of the above does not help, I'm afraid you'll have to change the battery completely. We have almost any battery for laptops.
DELL 9-pin battery connector pinout
A program for working with a laptop battery.
The process of repairing a laptop battery can be divided into two parts: replacing the elements and editing the contents of the EEPROM or the internal flash memory of the battery controller. If replacing elements is a simple process, accessible to any novice radio amateur who has basic skills in handling a soldering iron / spot welding machine, then programming the controller is a complex stage of work,
accessible only to a repairman with sufficient knowledge and experience. Battery EEPROM Works software is specifically designed to make second-stage battery repair as easy as possible. Battery EEPROM Works makes this step as easy as 1-2-3. The user only needs to connect the memory chip (EEPROM) to the adapter and press the RESET button. The program will do all the rest. The Full Charge Capacity will be the same as what you set before pressing the RESET button and will display the actual capacity of the new cells. The Cycles Count will be set to zero. The Manufacturer Date will be changed to the current date of your computer. The Permanent Failure Flag will be removed and all other necessary changes will be made. The data in the controller will be the same as in a new battery.
Battery EEPROM Works supports most laptop batteries from different manufacturers
Key Features
Reading SMbus data through the laptop battery connector.
Saving SMbus data to a text file.
Saving data in its own BQD format (BQ208X data file), for further use in cloning bq208X chips.
Reading and writing of all memory chips used in laptop batteries.
Reading and writing data from flash memory and EEPROM in integrated memory chips such as: BQ2083, BQ2084, BQ2085, PS401, PS402, BQ20Z70, BQ20Z80, BQ20Z90.
Saving data from flash memory and EEPROM in BIN format.
Resetting (zeroing) the parameters of the microcircuit to the original (factory) parameters with one click of the mouse.
Cloning password-protected chips with integrated flash memory (bq208X) into new or non-password-protected chips.
There are two options for resetting the laptop battery controller - using special programs or manually. This procedure should be carried out when the battery has been repaired, or when the software responsible for charging has malfunctioned.
Calibration using software
If you have changed battery systems, then this method will be very effective. Now you need to reset the controller, otherwise correct operation will be impossible. A program that will come in handy is called Battery EEPROM Works. Among its functions:
- Flashes the remaining capacity indicators. It must be set according to the corresponding value that the battery acquired after the repair.
- Resets the cycle counter to zero.
- The release date is set according to the one specified on your device.
After these manipulations, the battery starts working from zero. If you ignore calibration, there is a risk of damaging the battery itself, since the laptop will begin to turn off periodically.
Resetting the controller manually
In order to carry out manual calibration, special software is not needed, and professional skills are also not required. The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Disconnect the adapter from the network and reboot the device. Call the BIOS service before the system has fully booted.
- Now leave the laptop turned on. If it tends to overheat, then install a cooler first.
- After the laptop has turned off, you can plug in the adapter and wait until it is fully charged. Now the battery will work in the correct mode.
This method is suitable when problems arise with the software, but the battery itself does not need repair.
At one time, laptops gained immense popularity due to the ability to run on a rechargeable battery, which made it possible not to be confined to one place and to do the necessary work almost anywhere. The first models could last only a short time without a charge, and the nickel-metal hydride batteries used had a lot of disadvantages. But manufacturers did not sit idly by, and over several decades, battery manufacturing technologies have undergone dramatic changes. Today, the vast majority of laptops use lithium-ion batteries. They can last quite a long time and lack many of the disadvantages of their predecessors.
However, they are not perfect and may also become unusable over time. A battery malfunction means that it discharges very quickly, or the laptop does not display the charge level correctly. In this case, manufacturers and equipment sellers recommend purchasing a new battery. But, since the cost of the original component is quite high, you can try to correct its operation yourself. Depending on the degree of damage, it is necessary to either replace the battery cells, or it will be enough to reset the laptop battery controller.
It is the latter possibility that we want to talk about in more detail in today’s material. You can find out in what cases you need to reset the controller, and we will also tell you about possible ways on how you can do this yourself at home.
First, it's worth finding out what a battery controller is. This is a small chip built into the battery itself that controls its operating condition, as well as the charging and discharging process. It interacts with the power controller on the motherboard of the laptop itself, and also transmits the necessary system information to the operating system. We hope the diagram is clear to you. We tried to describe everything in simple words, but if you want to know the technical details, search the Internet.
When this small chip stops working correctly, you may need to reset the controller. This procedure is also popularly known as battery calibration. By and large, there are only two situations when this may be required: incorrect charge display and replacement of battery cells.
An incorrect charge display means a situation where the laptop’s operating system, even after a long charge, shows that the charge level is less than 100%, or the charge drops sharply, and the laptop turns off not after a few hours, as it should, but much faster. Many people begin to think that the battery has become unusable, but this is not always the case. The problem very often lies in its controller, which simply does not display the charge correctly.
By replacing battery elements, we mean that some workshops and service centers may offer so-called battery repacking, that is, replacing internal units that have become unusable. After this, the controller must be reset so that all new elements are recognized and can be used correctly. Although, if after replacing the blocks something does not work correctly, you have every right to make a claim and demand that the defects be corrected.
Now let's look at how to reset a laptop's battery controller. Let's touch on the software and manual methods.
Controller soft reset
On some sites you may see a recommendation to use the Battery EEPROM Works program. This is truly a very powerful and advanced utility that can, in some cases, literally revive the battery. But there is one big BUT! To use it, you need to know a lot and be able to understand electrical circuits, as well as have the necessary adapters, which are not always easy to get on the open market. We will not recommend this program for use in home devices, as it is very easy to permanently damage the battery. What then is right for you?

Battery EEPROM Works window
Almost every manufacturer has built-in power management utilities. It can be downloaded from the support site, on the driver download page for your device, and in some cases the utility can be either pre-installed or recorded on the included driver disk. Select the reset or calibration option and follow the on-screen instructions exactly. Most often, the utility discharges the battery to zero, after which it charges up to 100%. The controller will remember the extreme charge level indicators and will work as it did immediately upon purchase.
Manual controller reset
If for some reason you cannot find or install the power management utility, you can reset or calibrate the battery manually. How?
- Disconnect the laptop from the electrical outlet, and then switch it to BIOS mode. You can read more in the article on how to start BIOS mode.
- Leave the laptop and do not touch it until it is completely discharged. Take care that it does not overheat.
- Without turning on the laptop, put it on charge. Wait until it is fully charged; to do this, you can leave it overnight.
In 99% of cases, such simple steps will help bring the battery back to life. Well, if this doesn’t help, buy a new battery, or connect the laptop directly to the outlet, removing the battery.
- If you only use your laptop at home, then to reduce wear on its battery, it would be better to remove it. But before that, charge it to about 80% and also check the charge level from time to time as it is prone to self-discharge. After removing, connect the laptop to the power supply and use it like a desktop computer. This option is suitable for those who have a laptop in only one place, since with this use you can lose data if you disconnect the laptop from the power source while working.
- To increase the operating time of your device, set the appropriate parameters in the power plan settings. If necessary, use the power saving mode.
Conclusion
Friends, today we talked about how to reset a laptop charge controller. We learned that sometimes the problem lies not only in the hardware of the computer, but also in the software. Therefore, there is no need to rush to order a new battery right away. We hope everything worked out for you and there are no questions left. Don't forget to share your opinion in the comments.
Calibrating a laptop battery allows you to correct controller errors in which the actual battery capacity does not match the values determined by the system. As a result of this glitch, the battery life of the laptop is significantly reduced, causing inconvenience to users.
When to do it
Let's look at a specific example: the actual battery charge is 70%. Due to improper operation of the controller, the system displays 40% charge. When the system sees that the charge has dropped to 10%, the laptop will be sent to sleep mode. However, the actual battery capacity will not be 10%, but 40%, which means you could use the laptop offline for another hour.
To fix this error, you need to calibrate the battery. This procedure also helps to get rid of the “memory” effect, in which the battery “remembers” the charge level when the laptop is connected to the network, and subsequently releases energy to this limit, that is, the battery capacity is not fully used.
The "memory" effect occurs in nickel-cadmium (NiCd) and nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries; there is no such problem in lithium-ion batteries.
Determining battery capacity
Before calibrating the battery, check whether the battery requires such measures at all. This can be done using the command line:
If the last full charge is much lower than the maximum capacity, then you need to calibrate the battery. Recalibration will help eliminate a failure in the laptop battery controller. It is important to understand: the battery will not be restored to its original state, you will only eliminate the error due to which the battery capacity is incorrectly determined.
Automatic calibration
There are several ways to calibrate using special programs on different laptops.
Energy Management
Lenovo laptops have a special utility that allows you to calibrate the battery meter. All Lenovo Idea laptops are equipped with Energy Management software, which allows you to manage power supply.

The calibration process will take quite a long time - the battery will first be charged and then completely discharged. You cannot interrupt the operation, and it is also not recommended to use a computer.
Phoenix BIOS
Programs of this kind are also available on other laptops. HP laptops are equipped with a utility that allows you to check the condition of the battery and, if necessary, calibrate it, correcting the error in determining the charge level.
On some laptop models, a calibration program is built into the BIOS. Let's see how to calibrate the battery using the Phoenix BIOS as an example:

It is important that the power adapter is disconnected when performing the battery setup procedure. Otherwise, when you launch the utility in the BIOS, you will see a warning.
If you don’t find built-in calibration tools, you can download a universal program for all laptop models - BatteryCare, Battery Eater, etc. However, it is better to use standard tools, avoiding third-party software.
Manual calibration
If you do not have a program on your laptop that allows you to do calibration, and there is no way to download a universal utility, then you can perform the procedure for correcting the controller error manually. You can calibrate the battery in three steps:
- Charge the battery to maximum.
- Discharge it completely.
- Charge again to 100%.
The problem is that as soon as you unplug your laptop, its power plan will change. Once a certain low charge level is reached, the laptop will go into sleep mode, meaning it will not be able to completely discharge. Let's fix this shortcoming:

The plan you created will be selected automatically.
Another option is to log in and wait for the battery to drain. Almost all laptops do not have charge control in the BIOS, so the laptop will not be able to turn off on its own until the battery runs out.
To do the calibration, use the laptop until it turns off due to a completely discharged battery (power adapter is disconnected, the device is running on battery power only). Next, you should connect it to the network as soon as possible - it is harmful for the battery to remain in a discharged state for a long time.
After completing these steps, the controller failure will be resolved. Calibrating a laptop battery does not increase battery life - it is impossible to restore the physical wear of the battery using software methods. But the battery capacity will be determined correctly, which will allow you to use the available charge as efficiently as possible.
In this topic, post the software necessary for battery repair, information you need to know during repairs, typical faults and other necessary information, Do not ask questions in this topic.A little about batteries
Laptop battery. Accumulator battery (other names: accumulator, battery) - this is one of the main devices that distinguishes a laptop from a desktop machine, although this does not affect the operation of the laptop as such, but still you still want to have a working battery, at least so as not to turn off the laptop move from the room to the kitchen.
Let's see what kind of batteries there are in principle:
NICKEL-CADMIUM BATTERY - (or NiCd for short) nickel-cadmium;
NICKEL METAL-HYDRIDE BATTERY - (or NiMH for short) nickel-metal hydride;
LITHIUM ION BATTERY - (or Li-ion for short) lithium-ion batteries.
The latter are the most common and are considered to be the best batteries. Is it so?
Alkaline nickel battery technology was proposed in 1899, but the first NiCd battery appeared in 1947. At one time, these batteries were really almost the only ones. The emergence of newer electrochemical batteries, although it led to a decrease in the use of NiCd batteries, however, the identification of the shortcomings of new types of batteries led to renewed interest in NiCd batteries. The NiCd battery is like a strong and silent worker who works intensively without causing much trouble. The first thing that catches your eye is the weight and dimensions of the batteries. The NiCd battery is the largest and heaviest, being approximately twice as thick and heavy as the NiMH. It is harmful for NiCd batteries to remain in a charger for several days. In fact, NiCd batteries are the only type of battery that performs best when subjected to a full discharge periodically. All other types of batteries according to the electrochemical system prefer shallow discharge. So, periodic full discharge is important for NiCd batteries, and if this is not done, NiCd batteries gradually lose efficiency due to the formation of large crystals on the cell plates, a phenomenon called memory effect.
The appearance of NiMH was due to an attempt to overcome the shortcomings of nickel-cadmium batteries.
Eventually:
30 - 50% higher capacity compared to standard NiCd batteries;
less prone to memory effect than NiCd. Periodic recovery cycles should be performed less frequently;
less toxicity. NiMH technology is considered environmentally friendly.
However, there are also disadvantages:
Number of cycles: The number of charge/discharge cycles for NiMH batteries is approximately 500. Shallow rather than deep discharge is preferred. The durability of batteries is directly related to the depth of discharge;
Fast charge: NiMH battery generates significantly more heat during charging compared to NiCd. Additionally, a NiMH battery cannot charge as quickly as a NiCd; charging time is usually twice that of NiCd;
Self-discharge: Both NiMH and NiCd batteries have an acceptably high self-discharge. A NiCd battery loses about 10% of its capacity during the first 24 hours, after which self-discharge is approximately 10% per month. The self-discharge of NiMH batteries is 1.5-2 times higher than that of NiCd;
Capacity: The capacity of NiMH batteries is approximately 30% greater than the capacity of a standard (not very high capacity) NiCd battery of the same size;
Price: The price of NiMH batteries is approximately 30% higher than NiCd.
In 1970, the first commercial copies of primary lithium power sources appeared. Attempts to develop rechargeable lithium power sources were made back in the 80s, but were unsuccessful due to the impossibility of ensuring an acceptable level of safety when handling them. Research conducted in the 1980s revealed that during the charging and discharging of early lithium batteries, dendrites formed on the surface of the lithium. The growth of a dendrite to the positive electrode and the occurrence of a short circuit inside the lithium current source causes the element to fail. In this case, the temperature inside the battery can reach the melting point of lithium. As a result of the violent chemical interaction of lithium with the electrolyte, an explosion occurs. Thus, a large number of lithium batteries supplied to Japan in 1991 were returned to the manufacturers after several people suffered burns as a result of cell phone battery explosions.
Another type of popular battery is Lithium Polymer. The difference from Li-ion is inherent in the name itself and lies in the type of electrolyte used, it is understood that a dry solid polymer electrolyte is used, but today technology does not allow making such an element, so geleobra is used
a strong electrolyte, and as a result we get some kind of hybrid. Such batteries are neither pure li-ion nor Li-pol, and it would be more correct to call them lithium-ion polymer, but manufacturers call them lithium-polymer to promote batteries. As for the pros and cons of li-pol, they are exactly the same as those of li-ion, so further we will consider li-ion, because they are the most common today.
The advantages of a Li-ion battery include the absence of a memory effect. Once fully charged, a trickle charge is not required and the Li-ion battery can remain in the charger while not in use;
The disadvantage of a Li-ion battery is that it is subject to aging, even if not used. Capacity degradation occurs after about one year, and the battery often fails in the second and third year. Therefore, it is not recommended to store Li-ion batteries for a long time.
Enjoy them as much as possible while they are new. The maximum service life declared by element manufacturers is 5 years. Having become unusable, a Li-ion battery cannot be restored using charge-discharge cycles, as is the case with other types of batteries.
The only possible repair is to replace the battery elements, but there are some nuances here:
Laptop Lithium-ion batteries are implemented in the form of a sequential chain of elements, and an increase in capacity is achieved by parallel connection of the chains. When connecting batteries in series, there is a danger of overcharging the weakest of them; when connecting batteries in parallel, the difference in their internal resistance turns out to be significant: a battery with less resistance will be charged with a higher current. Both of these have a catastrophic negative impact on battery life. All battery cells must have the same parameters, so partial replacement of damaged cells with new ones will not lead to the expected result. Elements must also be from the same batch; elements from different batches have different parameters.
The above-mentioned danger of overcharging means the following: overcharging can lead to an increase in pressure in the element and depressurization. Therefore, the safety of battery operation is always ensured by a system of external electronic protection against overcharge and overdischarge of individual batteries. It includes controllers that measure the voltage of each battery or block of batteries connected in parallel, and a switch to open the electrical circuit when voltage limits are reached. Thermistors are used to monitor battery temperature.
Another disadvantage of Li-ion batteries is the fear of severe discharge (overdischarge). The above-mentioned protection circuit is powered directly from the batteries and therefore if the elements are completely discharged, the circuit stops working and the elements do not charge; in addition, a deep discharge negatively affects the internal structure of the elements themselves. It is believed that the optimal range for operation of li-ion cells is 20-100% charge; output below 20% leads to faster aging of the cells.
The service life of Li-ion cells is calculated not only in years of service, but also in charge-discharge cycles; as a rule, before the capacity is reduced by 20%, they provide 500 - 1000 cycles. It is quite difficult to predict the further behavior of the elements due to the large number of elements in the battery; most often there is a smooth decrease in capacity, sometimes abruptly, so the protection system keeps track of the number of cycles. On older battery models, when a certain cycle value was reached, the protection system closed the battery and it was not possible to use it. The possibility of closing the battery when a certain number of cycles is reached remains today, it’s just that the number of cycles prescribed in the battery is quite large, and the aging of the elements, and therefore the drop in capacity, occurs earlier. As a rule, the counter value can be reset, but do not forget that using such a battery is somewhat unsafe; the elements in the battery age unevenly, which means they are also charged and discharged unevenly.
There is another difficulty associated with the counter: what is considered a charge-discharge cycle? Full discharge and full charge? But it is not recommended to completely discharge it. Is it possible to read a short-term disconnection from the network in a cycle? Most modern batteries do not charge if the charge is currently greater than 90-95%, this avoids unnecessarily high rates of charge-discharge cycles. The figure 90%-95% is arbitrary - on some laptops it can be edited with special utilities.
As for storage conditions, there is no unambiguous information on this issue; the most common opinion is that it should be stored at a charge of 40% periodically (every two to three months), recharging to this value.
In general, Li-ion batteries function best at room temperature. Operating at elevated temperatures dramatically shortens their service life.
At low temperatures, battery efficiency decreases. A temperature of minus 20°C is the limit at which Li-ion batteries stop functioning
Battery repair is required in two cases:
1. The battery does not last long. She kept it new for an hour or two or three, and now it’s 5-15 minutes. Conclusion - bad elements. Options to solve the problem:
a) buy a new battery.
2. The battery does not hold at all. There are again two options:
a) buy a new battery
b) buy new cells and revive the battery yourself.
As you can see, there are few problems and few solutions.
Option b) New elements are definitely needed. 4-6-8-9-12 cell battery - accordingly you need 4-6-8-9-12 new cells. Simply replacing a dead group will not help. Why? The old elements have one capacity, the new one will have a different one. Accordingly, an imbalance will appear on groups of elements, and the electronics will simply turn off this battery.
Means:
1. ALL new elements are needed. It is recommended to set the capacity of the elements no less than the nominal one. Those. If you had 1800mAh cells - you can set 1800, 2000, 2100, 2200 mAh. There were 2000s - put 2000, 2100, 2200. Unless, of course, the difference in price is small. If this criterion is important (prices), then take elements of the native denomination.
2. Open the battery.
3. The elements must be welded in the same way as the original ones were welded. Look for people who have the appropriate equipment. You can't just solder. Some people say “not recommended”, but believe me - NOT.
4. You need to disconnect elements from the electronics from the largest plus to the smaller. In most cases this can be determined visually. If it doesn’t work, arm yourself with a tester.
5. Before welding the elements, connect them all together overnight: all the pluses to the pluses, the minuses to the minuses. This is necessary to equalize the potential on the banks.
6. The battery is opened, new elements are purchased, welded in the likeness of the old ones, the old ones are removed... In theory, all that remains is to solder the new elements to the electronics, and hurray!!! No, no cheers. It's all about the same electronics. It remembers everything about your old elements - the number of cycles performed, the capacity of the elements, etc. If your battery had a capacity of 4000 mAh, and after a year or two or three of operation its capacity became 200 mAh, then even if you insert new elements into the battery, the electronics “will not believe it”. Convincing electronics that it has new elements is called flashing (resetting, resetting) the firmware. For what tools to do this, see the section “HARD - hardware that is necessary for repairing laptop batteries”
7. Now you need to determine which bundle you will be dealing with. The term “bundle” appeared due to the fact that, as a rule, a pair of microcircuits are used in electronics: a control controller and a memory in which various useful data are stored. There are batteries whose electronics contain only memory, or only a controller. But out of habit, we will continue to call them “bundles”. Look carefully at the electronics board. The controller is usually the largest chip on the board. Memory is, as a rule, an 8-pin microcircuit, for example, series 24C64, 24C32 and the like.
8. The link has been identified. Now the question is what and where to change in order to reset the firmware. Some controller manufacturers do not hide this information and describe everything in detail in datasheets. By reading and understanding the datasheet for your controller, you will know what needs to be changed and what. In some cases, battery manufacturers hide the information, and it is obtained bit by bit. But then it is embodied in programs that can be used for repairs.
9. We connect the elements to the electronics from “ground” to “plus”. Those. first the “ground”, then the “plus” of the first element, then the second, etc. - until the very last.
10. Battery assembly, firmware reset. It's time to insert the battery into the laptop (I recommend sticking it with tape until you get 100% success) and try to charge it. If the battery takes a charge (which can be seen either by the indicator on the laptop or by the Windows software indicator, or even better, use the BatMon program). We wait until the battery charges to 100%. Next: in Windows, in the power supply properties, we create a new scheme (test), in which nothing is ever turned off: neither the screen, nor the hard drive - nothing at all. We also turn off all alarms. Launch BatMon, unplug the power plug from the laptop and enjoy the discharge curve. It should fall evenly and smoothly. If it went down sharply, it means you made a mistake in reflashing. If it drops evenly and then falls through, it means you have acquired bad elements. After the laptop turns off, put it on charge again. It is recommended to charge and discharge the battery two or three times.
Please note that during the first discharge the following is possible: the curve will quickly drop down, and then the laptop can work at zero percent for a long time (this is why we disabled the laptop’s self-shutdown). No need to panic. It’s just that after the first time, the electronics have not yet “determined” the extreme points of charge and discharge of the elements. That is why it is recommended to carry out a couple of charge-discharge cycles - so that the electronics work correctly. If after several cycles this does not happen, it means that an error was made somewhere.
11. So, if the goal is achieved: the laptop runs on battery for the required hour or two or three (like new), the charge and discharge curve is uniform - then we can be proud of ourselves and consider that we have achieved success.
A program for working with a laptop battery.
The process of repairing a laptop battery can be divided into two parts: replacing the elements and editing the contents of the EEPROM or the internal flash memory of the battery controller. If replacing elements is a simple process, accessible to any novice radio amateur who has basic skills in handling a soldering iron / spot welding machine, then programming the controller is a complex stage of work,
accessible only to a repairman with sufficient knowledge and experience. Battery EEPROM Works software is specifically designed to make second-stage battery repair as easy as possible. Battery EEPROM Works makes this step as easy as 1-2-3. The user only needs to connect the memory chip (EEPROM) to the adapter and press the RESET button. The program will do all the rest. The Full Charge Capacity will be the same as what you set before pressing the RESET button and will display the actual capacity of the new cells. The Cycles Count will be set to zero. The Manufacturer Date will be changed to the current date of your computer. The Permanent Failure Flag will be removed and all other necessary changes will be made. The data in the controller will be the same as in a new battery.
Battery EEPROM Works supports most laptop batteries from different manufacturers
Key Features
Reading SMbus data through the laptop battery connector.
Saving SMbus data to a text file.
Saving data in its own BQD format (BQ208X data file), for further use in cloning bq208X chips.
Reading and writing of all memory chips used in laptop batteries.
Reading and writing data from flash memory and EEPROM in integrated memory chips such as: BQ2083, BQ2084, BQ2085, PS401, PS402, BQ20Z70, BQ20Z80, BQ20Z90.
Saving data from flash memory and EEPROM in BIN format.
Resetting (zeroing) the parameters of the microcircuit to the original (factory) parameters with one click of the mouse.
Cloning password-protected chips with integrated flash memory (bq208X) into new or non-password-protected chips.
![]()
![]()
Mobile computer batteries love to surprise their owners. After working as expected for 1-2 years, they begin to do strange things: then, showing a full charge, they do not allow the laptop to turn on for even five minutes; then in a matter of seconds they are charged from 0 to 100% and at the same speed are “blown away” back to zero.
Sometimes such tricks are carried out by batteries that are far from old and still work. It’s just that over time they “forget” about their real capacity and display a percentage of charge that is not what it actually is. To “refresh your memory” a calibration procedure is shown for these capricious devices.
Today we’ll talk about what calibrating a laptop battery is and how it should be done. To make it clearer, let’s first get acquainted with the design of batteries and the functioning of their charging system.
Design and features of laptop batteries and their charging systems

All mobile computers, with the exception of rare long-lived ones, have rechargeable batteries of the lithium-ion (Li-ion) or lithium-polymer (Li-po) type. Why them? Here are 4 qualities that make manufacturers choose them:
- High charge density (capacity or amount of energy that a battery can hold) in a small size. This allows you to achieve good autonomy of the device without increasing its dimensions and weight.
- Possibility of charging and discharging with high currents. The charging speed depends on the current value, that is, lithium batteries can be charged quickly. They also transfer large currents to laptop devices without harm.
- Slight self-discharge (reduction of charge when disconnected from the load through internal resistance). If the battery is not used for some time, its charge level decreases slightly.
- No maintenance required. To ensure that the laptop battery does not fail before the deadline, which occurs after 2.5-5 years of use, the owner only needs to follow the rules of its operation and calibrate it from time to time.
The laptop battery consists of 6-8-12 batteries or “cans”, which externally resemble AA batteries. The nominal voltage of one element is 3.6 V (3.7 V for Li-po), the actual voltage is about 3.9-4.2 V. This voltage indicator is taken as 100% charge.
“Banks” of 2-3 pieces are connected in parallel into cells. With this type of connection, their capacities are summed up. The cells are connected to each other in series. When connected in series, their voltage is summed. By changing the number of elements and methods of connecting them, manufacturers create batteries of different output voltages and capacities.

The actual output voltage of a typical 3-cell mobile computer battery is 10.8–12.6 V, and a 4-cell battery is 14.8–17.2 V.
The same battery contains “cells” with the same nominal characteristics, but their physical properties, such as capacity and charging speed, usually differ. A special device, the battery controller, which is located inside the battery, ensures that the cells are charged strictly to the required level and do not “grab” too much.
Each cell is connected to the controller contacts by balancing wires, through which it receives voltage information. If one group of elements has already reached the upper threshold, but the rest have not, the controller turns it off from the energy supply. This is done not only to optimally fill the container, but also to protect the cells from overcharging, which can cause a fire or even explosion of the battery.

For lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries, too strong a discharge is harmful - below 0% or 3.3–2.7 V. Overdischarge can lead to a significant decrease in capacity, and in the worst case, to a complete impossibility of charging due to blocking of the controller . Locking is an emergency measure to prevent further discharge and complete failure of the battery, but removing the controller from it is very difficult. Especially at home.
In addition to the controller built into the battery, the laptop has another system that controls the charging process. The central link of this system is the charger microcircuit. It is located on the motherboard and is a PWM controller, which, receiving information about the state of the battery and power supply, opens and closes transistor switches that switch energy supply channels.

The tasks of the internal charge control system include:
- Determining whether the battery is connected to the computer.
- Recognizing the type and capacity of the battery, generating the current and voltage levels needed to charge it.
- Monitoring charging current and voltage levels.
- Stop charging the battery when it reaches 100%.
The ability to power the computer from the battery ensures the joint operation of all components - from “cans” to elements on the motherboard. Malfunctions of any link lead to early loss of battery capacity, making it impossible to charge it or power the device from it.
What is battery calibration and what is the benefit of it?

If you have ever used devices powered by nickel-based batteries, you may be aware of the memory effect - a temporary decrease in battery capacity due to recharging it before it is completely discharged. Such batteries remember the voltage threshold at which they were connected to the power source, and during the next operating cycle they take it as 0%. To eliminate this effect, the battery must be completely discharged and recharged to 100%. This process is called calibration.
Lithium power supplies do not have a memory effect, but they also require periodic calibration. The reason is desynchronization of charge level data on the internal and external controllers, which occurs after multiple cycles of incomplete charging and discharging. The calculation error is about 1% per cycle and accumulates over time. At the same time, the control system begins to “think” that the battery capacity is lower than it actually is.
Manufacturers of lithium batteries for mobile computers recommend calibration once every 3 months, but this is not a strict rule. You can do this more often or less often, depending on how you use the battery.
How to properly calibrate the battery
A full laptop battery calibration cycle takes several hours. In addition, to enhance the effect, it is carried out with a 5-8 hour break. During this time, the battery “rests” and is restored. Therefore, it is best to carry out the procedure before going to bed or leaving home, for example, to work.
To carry out calibration, the capabilities of the operating system are sufficient, but if desired, this can be done using programs, which will be discussed below, as well as a specialized utility built into some versions of BIOS.
The procedure for calibration using the operating system
- Charge the battery to 100% and let it hold the charge for 1-2 hours, that is, leave the power supply connected to the laptop. During this time, you can use the device as usual, but not too intensively so that the battery does not heat up.
- Disconnect the power supply cable from the laptop. Open the control panel section " Power supply" and click " Setting sleep mode».

- Then click " Change advanced power settings».

- In the list of additional parameters, open the section " Battery" Assign " The effect of an almost completely discharged battery" when powered by battery, the value is " Hibernation", and in the section " Battery level is almost completely discharged» when powered by battery, set the lowest possible value, optimally up to 5%. After saving the setting, when the charge drops to the specified level, the laptop will automatically enter the hibernation state.

- Keep the computer turned on until the battery reaches its minimum level, then shuts down. During this time, you can continue to work, but not too intensely, so as not to heat the battery. After disconnection, at least 5 hours must pass before the battery is reconnected to the power source. If it is not possible to keep the laptop turned off, remove the battery from it.
- Connect the laptop to the mains and charge the battery to 100%, being careful not to interrupt this process. You can use the device while charging.
After calibration you will know the actual capacity of the battery. If it has not exhausted its resource too much, the capacity will be higher, sometimes by tens of percent. However, along with it, the level of battery wear will also increase (many monitoring utilities display this). Don’t be afraid of this phenomenon: calibration does not damage the battery or accelerate its wear, it’s just that after it all indicators come closer to the true values.
Calibration via BIOS
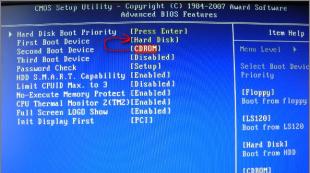
The battery calibration tool, which is built into certain BIOS versions, is called “ SmartBatteryCalibration"and is located in the Boot section. In some Russian-language versions of UEFI this function is also called " Testingbattery»

According to experts, calibration using BIOS is more effective and correct than in the operating system, since outside the OS the lower threshold for battery discharge approaches zero. However, this method is less convenient for the user, since during execution, which can last 3-5 hours, working on a laptop is impossible.
How to calibrate using Smart Battery Calibration:
- Unplug the laptop from the power outlet.
Why are they given so little attention in the article? Because they are mentioned more for reference. I don’t recommend installing, much less buying, them for this task, because they essentially automate something that can be done by hand, and the result of their work is not always satisfactory. It is easier and more reliable to use operating system tools or BIOS functions to calibrate batteries, where possible.
Also on the site:
Calibrating a laptop battery: what is its meaning and how to do it correctly updated: March 13, 2018 by: Johnny Mnemonic
Let's see what kind of batteries there are in principle:
- NICKEL-CADMIUM BATTERY - (or NiCd for short) nickel-cadmium;
- NICKEL METAL-HYDRIDE BATTERY - (or NiMH for short) nickel-metal hydride;
- LITHIUM ION BATTERY - (or Li-ion for short) lithium-ion batteries.
Lately batteries have been used Li-ion
The first thing you need to do is calibrate the battery. In fact, this is the calibration of the controller.
First you need to completely discharge the battery - turn off the power supply, reboot, intercept the boot (so that the OS does not boot) by calling the BIOS setup.
Place the laptop on its end like a slightly open book (for better cooling, with the muzzle up if it is on the side) and leave it until it turns off until the entire battery is drained.
Typically, the controller notes both events (full discharge and full charge), after which it begins to count the charge correctly - until a charge measurement error occurs again.
If all of the above does not help, I'm afraid you'll have to change the battery completely. We have almost any battery for laptops.
DELL 9-pin battery connector pinout
A program for working with a laptop battery.
The process of repairing a laptop battery can be divided into two parts: replacing the elements and editing the contents of the EEPROM or the internal flash memory of the battery controller. If replacing elements is a simple process, accessible to any novice radio amateur who has basic skills in handling a soldering iron / spot welding machine, then programming the controller is a complex stage of work,
accessible only to a repairman with sufficient knowledge and experience. Battery EEPROM Works software is specifically designed to make second-stage battery repair as easy as possible. Battery EEPROM Works makes this step as easy as 1-2-3. The user only needs to connect the memory chip (EEPROM) to the adapter and press the RESET button. The program will do all the rest. The Full Charge Capacity will be the same as what you set before pressing the RESET button and will display the actual capacity of the new cells. The Cycles Count will be set to zero. The Manufacturer Date will be changed to the current date of your computer. The Permanent Failure Flag will be removed and all other necessary changes will be made. The data in the controller will be the same as in a new battery.
Battery EEPROM Works supports most laptop batteries from different manufacturers
Download: You cannot download files from our server
Key Features
Reading SMbus data through the laptop battery connector.
Saving SMbus data to a text file.
Saving data in its own BQD format (BQ208X data file), for further use in cloning bq208X chips.
Reading and writing of all memory chips used in laptop batteries.
Reading and writing data from flash memory and EEPROM in integrated memory chips such as: BQ2083, BQ2084, BQ2085, PS401, PS402, BQ20Z70, BQ20Z80, BQ20Z90.
Saving data from flash memory and EEPROM in BIN format.
Resetting (zeroing) the parameters of the microcircuit to the original (factory) parameters with one click of the mouse.
Cloning password-protected chips with integrated flash memory (bq208X) into new or non-password-protected chips.